Test-Driven Development (TDD) has been a cornerstone of agile software development, promoting a cycle of writing tests, coding to pass tests, and refactoring. However, as projects grow in complexity, traditional TDD sometimes falls short in addressing broader design and system-level issues. Enter Double Loop TDD, an advanced methodology that builds on the foundations of TDD to offer a more comprehensive development approach.
What is Double Loop TDD?
Double Loop TDD extends the conventional TDD cycle by introducing an additional loop that focuses on the system's behavior and design. While traditional TDD (the inner loop) emphasizes writing unit tests and implementing code to pass these tests, Double Loop TDD (the outer loop) emphasizes behavior-driven development (BDD) and architectural concerns.
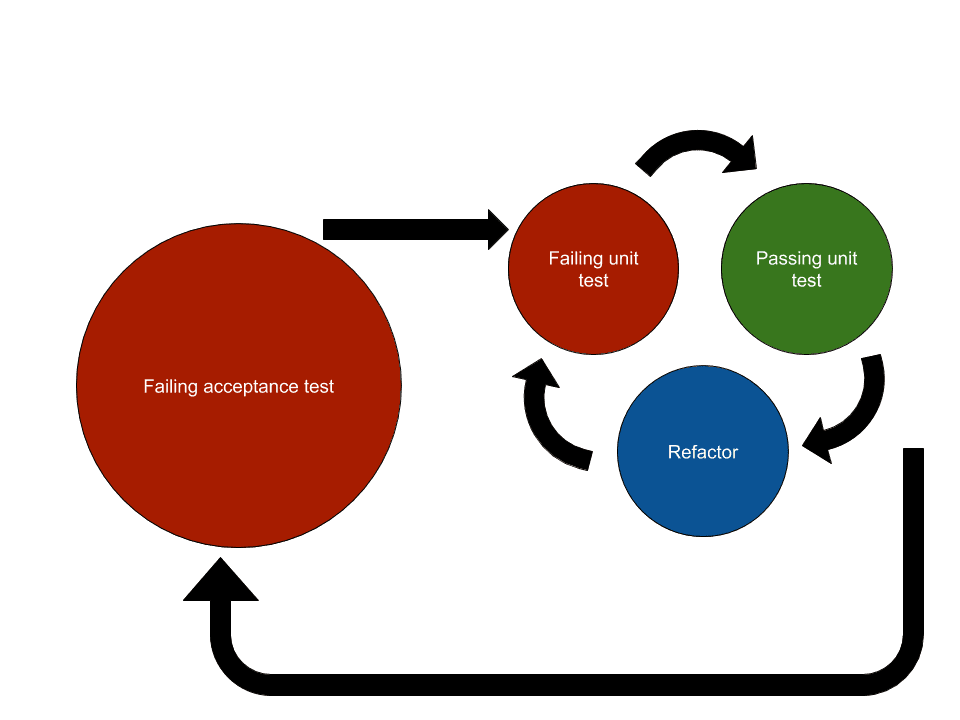
The Inner Loop: Classic TDD
- Write a Failing Unit Test: Identify a small piece of functionality and write a test that describes how it should behave.
- Write Code to Pass the Test: Implement the minimal amount of code necessary to make the test pass.
- Refactor: Improve the code quality without changing its behavior, ensuring it is clean and maintainable.
The Outer Loop: BDD and Architectural Focus
- Define a User Story or Feature: Using BDD principles, describe a high-level behavior or feature from the user’s perspective.
- Write Acceptance Tests: Create tests that validate the feature or user story, ensuring it meets the specified behavior.
- Design and Implement: Architect the system components required to pass the acceptance tests.
- Refactor: Improve the system design and architecture without altering its external behavior.
Why Double Loop TDD?
Comprehensive Coverage
Double Loop TDD ensures that both micro-level functionality and macro-level system behavior are tested and validated. This dual focus helps catch issues that might be missed by traditional TDD alone, particularly those related to system integration and overall design coherence.
Enhanced Design Quality
By incorporating BDD and a focus on architectural design in the outer loop, developers are encouraged to think about the system’s structure and user interactions early in the development process. This leads to better-designed software that is easier to maintain and extend.
Improved Communication
The BDD aspect of Double Loop TDD fosters better communication between developers, testers, and non-technical stakeholders. User stories and acceptance tests written in natural language can be easily understood by all parties, ensuring everyone is aligned on the project’s goals and requirements.
Implementing Double Loop TDD
Step 1: Start with the Outer Loop
Begin by defining a high-level user story or feature using BDD principles. Collaborate with stakeholders to ensure the story accurately reflects the desired behavior. Write acceptance tests that describe the expected outcomes.
Step 2: Dive into the Inner Loop
For each acceptance test, identify the unit tests needed to implement the required functionality. Follow the classic TDD cycle: write a failing unit test, implement the code, and refactor.
Step 3: Integrate and Validate
After implementing the necessary unit tests and functionality, run the acceptance tests to ensure the feature behaves as expected. If the tests pass, proceed to refactor the system’s architecture, improving its overall design and maintainability.
Step 4: Iterate
Repeat the process, moving back and forth between the inner and outer loops. Continuously validate individual components and overall system behavior, refining both as the project evolves.
Challenges and Considerations
Learning Curve
Double Loop TDD introduces additional complexity and requires a good understanding of both TDD and BDD. Teams may need time to adapt to this methodology and integrate it effectively into their workflow.
Tooling and Frameworks
Leveraging appropriate tools and frameworks is crucial for successful Double Loop TDD. Popular BDD frameworks like Cucumber or SpecFlow can be integrated with TDD tools to facilitate this process.
Balancing Granularity
Striking the right balance between the inner and outer loops can be challenging. Too much focus on unit tests may overlook system-level issues, while excessive emphasis on the outer loop might lead to neglecting detailed unit testing.
Conclusion
Double Loop TDD offers a powerful approach to software development, combining the rigor of TDD with the holistic perspective of BDD. By addressing both detailed functionality and overall system behavior, it ensures robust, well-designed, and maintainable software. Adopting Double Loop TDD can lead to higher quality outcomes, improved stakeholder communication, and a more agile development process.
Embrace the double loops, and take your development practices to the next level.